Steering towards Sustainable Roadbuilding
As towns and cities expand their
infrastructure, the demand for better transportation grows. Whilst roadbuilding
is certainly not on the list as one of the most sustainable sectors of
construction – largely due to the negative impact the production of asphalt has
on the environment – changes are being made in the industry to ensure it is
working towards an environmentally conscious future.
Climate
agreements and stringent regulations issued by governments and authorities
worldwide are posing increased challenges for the asphalt industry concerning
reducing greenhouse gases, such as CO2.
Many markets are phasing out coal as a
fuel, while systems running on oil are subject to these regulations and
restrictions says Benninghoven. In moves to work toward a more sustainable
future, Benninghoven technologies have enhanced their Evo Jet multi-fuel
burners, which can use renewable fuels such as biomass to liquid (BtL) and wood
dust, in addition to both having a carbon neutral footprint.
Owners
of asphalt mixing plants need to be conscious of driving down emissions to help
secure the future of the plant site. Changing from oil or coal dust to gas is a
major step says Germany-based Benninghoven – the use of natural gas or liquid
gas already halves the CO2 emissions.
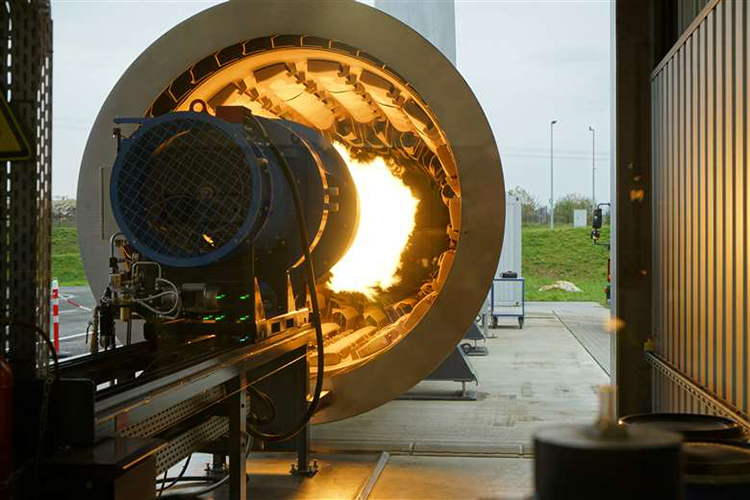

Benninghoven’s Evo Jet wood dust burner
allows wood dust to be used in asphalt mixing plants. Engineers at Benninghoven
are said to have identified the ideal particle size of the wood dust, which is
produced from scrap wood and wood waste.
The
fuels of the future, wood dust and biomass to liquid, are attractive when it
comes to their availability, as fossil fuels are not only limited but are
becoming increasingly more difficult to produce. Benninghoven says that this
makes it even more important that plant owners use the right technologies to be
prepared for the future by using alternative fuels.
Lowering emissions has driven machine
development in recent years, and this has been a key focus for Benninghoven.
Among
the company’s advances in the application of low-temperature asphalt, which
although not new, has become the focus of road construction authorities today.
The demand for balancing CO₂ levels, conserving resources, and reducing energy
are driving innovation and asking companies across the sector to develop their
capabilities.
It
was formally requested in August 2021 by National Highways that everyone
involved in the construction and maintenance of the strategic road network,
particularly designers and main contractors, use low-temperature asphalt as their
default surfacing material to help achieve net zero.
Low-temperature asphalt is a mixture that
requires a production temperature between 110° and 130°. Hot asphalts, on the
other hand, are produced at a temperature range between 140° and 180°, although
160° with hot bitumen as a binder is most common. The advantage is that the
production and the processing of low-temperature blends can be conducted
conventionally.
According
to the German Asphalt Association, a temperature reduction of just 30 °C saves
0.9 litres of fuel oil (or equivalent fuel) per ton of finished asphalt; a
daily production of 2,000 tons of mixture thus saves 1,800 litres of oil or up
to three-quarters of the annual energy consumption for heating a house – the
reduction in CO₂ emissions is 6,000kg per day.